A financial statement is simply a snapshot of your business finances. It is a financial document that summarizes the financial position of a business entity and includes an analysis of its performance over time.
As with any business analysis, a financial statement is only as good as the information and data available.
The accountant’s responsibility is to prepare the financial statement to ensure that the information provided is complete and accurate.
Preparing a financial statement can also require a lot of time and resources, so a clear and concise statement of the material data and facts is essential.
In the modern business environment, businesses must present accurate and complete information to their customers, investors, suppliers, and creditors.
This is why listed companies must publish a full set of audited financial statements by statute. The full set of audited financial statements comprised of:
- Statement of Comprehensive Income or Income Statement
- Statement of Financial Position or Balance Sheet
- Statement of Cashflows
- Statement of Changes in Equity
Let us now take a look at each of these statements individually.
Statement of Comprehensive Income
Statement of comprehensive income(SOCI), also known as a statement of income, is the formal accounting term for a company’s annual report on its profitability.
The SOCI shows the profit and loss statement for a company.
The statement of comprehensive income gives information about the
- Sales revenue
- Cost of sales
- Expenditures
- Administrative expenses
- Operational expenses
- Selling expenses
- Interest expense
- Tax expense
The SOCI is one of the fundamental documents used by stakeholders to assess the financial profitability of a business.
By assessing the information regarding the revenue generated, cost of sales, expenditures incurred, and the profit or loss for the period, the stakeholders can learn whether a business is worth investing in.
Prepared on Accruals basis
The SOCI is prepared on the accruals basis of accounting, which means that the data included in SOCI reflects the income that is earned but may not have been realized and, similarly, expenditure that has been incurred but not yet paid out.
Format of a SOCI
The line items of a SOCI may vary from one business to another, but the general format remains the same for every business.
Companies may release their SOCI and comparative figures for the previous years if required by law or under company policy to provide complete disclosure for the stakeholders.

The SOCI is used to drive and calculate profitability ratios of metrics, which are also used as KPIs by companies for benchmarking their progress.
Statement of Financial Position
The most basic type of financial statement is the statement of financial position (SOFP) or balance sheet.
This document reports the financial position of the business entity and provides information about its assets, liabilities, and equity at the year-end date.
Prepared on a Cash basis
While the SOCI presents data on an accruals basis, the SOFP presents data on a cash basis, which means that all balances shown in the balance sheet are year-end balances of what the business owns or owes.
Format of SOFP
The balance sheet shows the financial position of the business entity at the year-end date. It can therefore be used to calculate the liquidity and leverage of the company.
SOFP is the go-to document for various stakeholders, including banks and investors, when they want to find out about the investment’s long-term viability.
Like SOCI, a company may publish its SOFP with comparative figures for previous years to follow statutes or disclose information better to the stakeholders.
The format of a SOFP is as follows.
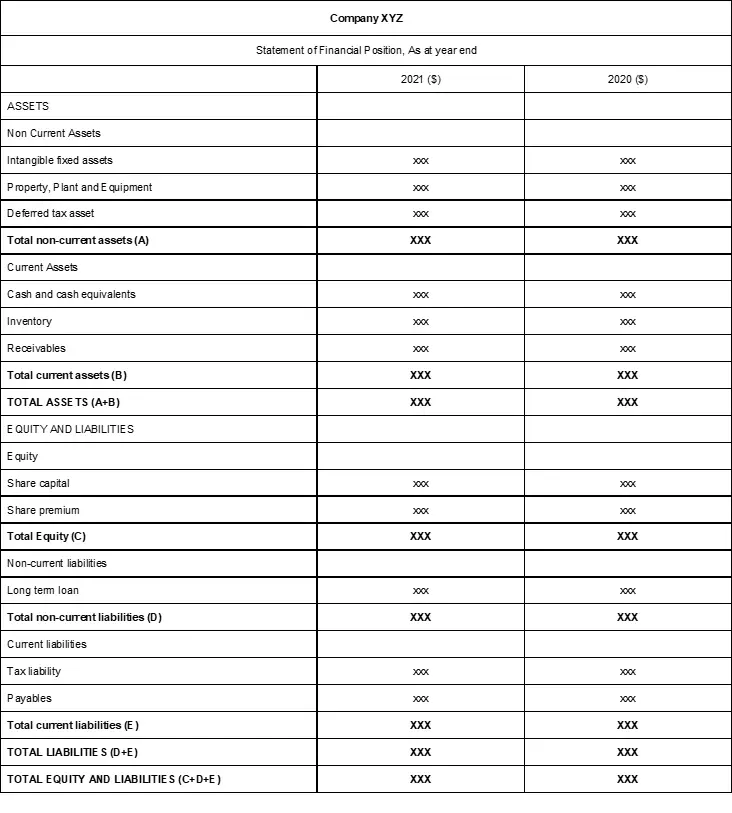
Stakeholders and investors can use the balance sheet to calculate liquidity and gearing ratios to assess a company’s long-term viability and financial strength.
A company with a loss in the SOCI may still be desirable for investment if it has a strong balance sheet.
Statement of Cashflow
A cash flow statement or also known as a statement of cash flows or statement of cash flows statement of operations, is a statement that provides information about a company’s cash flows during the year.
The cash flow statement is one of the main financial statements of a company that stakeholders turn to after the SOFP and SOCI, and it summarizes the company’s cash flows in a given period.
It gives a detailed breakdown of the sources and uses of cash throughout the period. The statement shows the cash inflows and outflows of the company and is a tool used to analyze and compare the company’s performance.
At a quick glance, the cash flow statement can be used to determine a company’s liquidity position. The cash flow statement is divided into three sections namely.
- Cashflow from operating activities: Contains only the inflow and outflow of cash related to the operating activities of the business. All non-cash expenses have to be added back to the profit, as non-cash expenses do not indicate an outflow of cash.
- Cashflow from investing activities: All cash inflow and outflow must go under this heading. This includes sales and purchase of non-current assets and other items that may be classified as investing activities.
- Cashflow from financing activities: All cash inflow and outflow about financing activities of the business should go under this heading, including paying off loans, an inflow of debt, share proceeds, etc.
Cashflow format
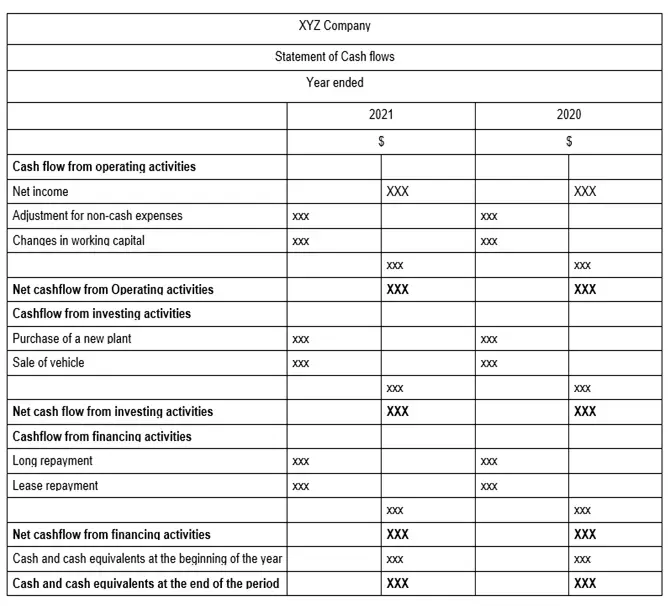
Statement of Changes in Equity
The statement of changes in equity is also known as the retained earnings statement. It is a statement that shows the end-of-year position of the changes in the owner’s equity for a company.
The movements in owners’ equity can be due to
- Net profit or loss
- Share issue
- Dividend payments
- Gains or losses that are recognized directly in equity
- Correction of error
- Changes in accounting policy or estimate
The image below shows the statement of Apple Inc’s equity changes.
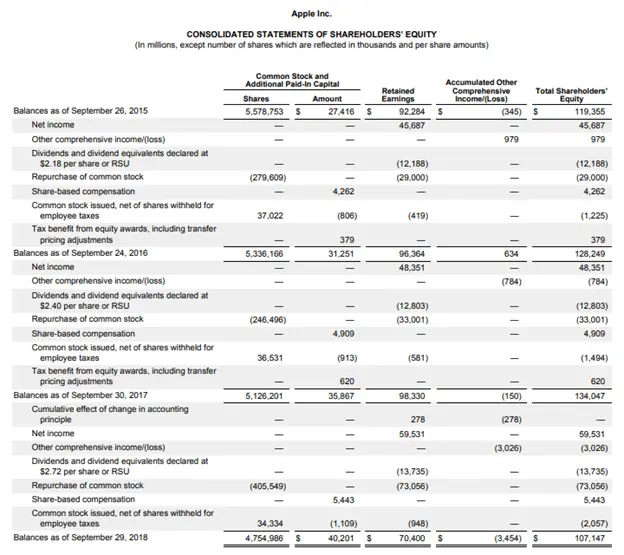
It can be seen how each item that causes any change to the equity portion of the balance sheet is adjusted to reflect the correct position of the items relating to business equity at the year-end date.
Together these four financial statements make up the complete set of financial statements required to be published by listed entities.
In addition to these four statements, companies also publish additional notes to financial statements that contain explanations, calculations, and other relevant information about the items contained within the four statements discussed above.
