Definition:
A corporate spin-off can be defined as the creation of a new stand-alone business by selling or distributing shares from the existing business. The parent company will spin off a business if it believes the new business will be worth more independently. The Spin-off is also called star bust or spin out.
The spin-off companies retain the same assets, H.R and IP but the management of the company changes, it also takes up a new name. The corporations will spin off a part of their company if they believe the newly created business will be more lucrative as a spin-off.
Some Famous examples:
Paypal was spun-off from eBay. Kioxia (a memory chip business) was spun off from Toshiba after it ran into financial troubles. Both spin-offs have performed magnificently and Kioxia was recently looking for an IPO on the Japanese stock exchange.
Why do a Spin-off?
There are many reasons why a corporation would do a spin-off. Some of the main reasons are:
1) The company has run into financial troubles and is looking to raise capital by doing a spin-off of its attractive assets.
2) The company believes the stand-alone spin-off will be worth more than the combined value of the company.
3) The company is looking to unlock shareholder value.
4) A new segment of the company is growing very fast and to maintain this growth and curb bureaucratic slowdown; it is spun-off.
There may be multiple other reasons for a spin-off. It is evaluated on a case-by-case basis.
Advantages of a Spin-off
The main advantages of a spin-off in figure 1 below.
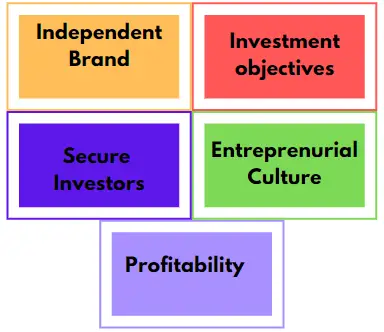
Figure 1: Main advantages of a spin-off
A company is able to create an independent brand that will have its own attractiveness to the consumer. Sometimes, investors are not satisfied with the company’s performance and to satisfy them, a company may spin-off to fend off the pressure from the investors.
A spin-off company is able to follow its own trajectory for a long-term investment plan without any pressure from the parent company. The company is also able to develop its own unique corporate culture that best helps it fulfills its needs.
Disadvantages of a spin-off
If a spin-off has some advantages, it also has some disadvantages. The main disadvantages are highlighted in figure 2.
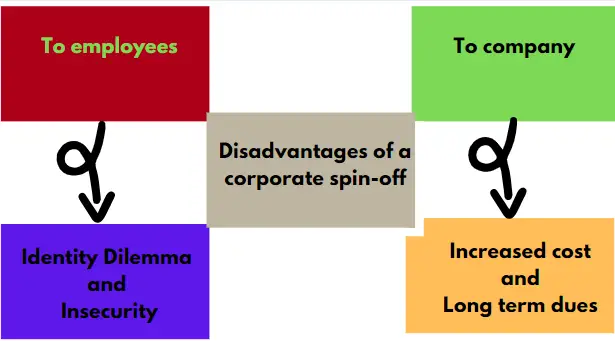
Figure 2: Main disadvantages of a corporate spin-off
The disadvantages of a corporate spin-off are divided into two main parts as shown in figure 2. The number 1 is the increased costs to the parent company, these may include legal fee and obligation dues, while number 2 is what impacts the employees, the employees feel dissatisfied, anxious, and insecure. The company must keep these in mind when planning a spin-off.
The process of a spin-off
There are many complex legal and regulatory issues that may plague a spin-off. The company must keep all these in mind when planning a spin-off. Each spin-off has its own process and the process may differ from one spin-off to another, but an overview of the spin-off is shown in figure 3. Each step is explained in detail below:
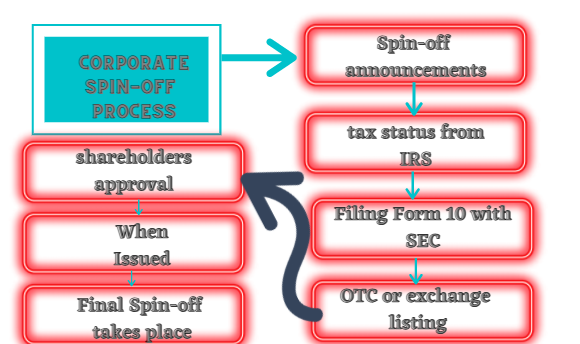
Figure 3: Main process of a spin-off
1) Spin-off announcement:
First of all, the spin-off has to be announced and proportional shares are to be distributed. The proportional share distribution is the distribution of shares of the newly created spin-off to the existing shareholders.
A detailed plan is created as to how these shares of the newly created spin-off will be distributed. Normally, the biggest shareholders of the parent company get the most shares in the newly planned spin-off.
Sometimes, a company may stop the spin-off at this stage due to the revolt of the shareholders. The company sometimes tries to spin off attractive assets which the shareholders do not want to do.
2) IRS and spin-off
This is a simple regulatory requirement. It helps in the evaluation of any tax liabilities or tax write-offs the new spin-off company may have.
3) Filing Form 10 with SEC
This is also a regulatory requirement. Form 10 filing with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) which is required to list the company on a U.S. Exchange. If a company has more than ten million dollars in assets and over 750 shareholders, it is required to file Form 10.
4) Application process for OTC or listing on the exchange
OTC stands for over-the-counter trading, this is done for companies not listed on a formal exchange. Sometimes, the spin-offs are not listed on the exchange, but the shares are sold to a list of private investors. The spin-off may also be listed on a stock change.
It really depends upon the preference of the parent company. So, before any of these take place, a formal application has to be filed.
5) Shareholders’ Approval
This is a big requirement for the public listed companies. A lot of times, a spin-off collapses at this stage. As stated before, sometimes a company may try to spin off its most attractive assets that cause a shareholder revolt. So, it is very important to get shareholders’ approval.
6) When Issued (WI)
When issued or WI is when the spin-off has gotten thumbs up from the regulator, but the issues have not been yet shared for the spin-off. WI may also be canceled.
The parent company uses WI to raise capital before the issuing of stock of the new spin-off. It helps the parent company pay off any of its dues or fees associated with the spin-offs.
7) Final Spin-off takes place
After clearing all the hurdles, the spin-off can finally take place. This is the final stage in the process of a spin-off. A new entity is created that can now operate independently.
Conclusion
There are many reasons that a parent company may do a spin-off of its assets. It all depends upon the needs of the particular parent company. The regulatory and legal requirements are extremely complex and a spin-off can fail at any stage in the spin-off process. Many spin-offs have been a roaring success, while few have also failed miserably.
