A cash receipt is issued when a cash transaction takes place and the payment is made through cash or cash equivalent.
A cash receipt is an integral part of any accounting system. It has several uses including records for cash sales, balancing accounts receivable and payable, and reconciliation of accounts.
Let us discuss the cash receipt format and its uses along with the cash receipt journal.
What is Cash Receipt?
A cash receipt is a statement of the amount of cash received in a cash sale transaction. It is created with multiple copies for record-keeping purposes.
A cash receipt includes several key information points including date, amount, and customer name. A cash receipt is an important document for accounting record purposes.
The cash receipt involves transactions that are paid in cash as well as through cards. A cash transaction means transferring of balance immediately. The transfer can take place through cash or card payment methods.
Cash transactions can include spontaneous cash sales or accrual cash transactions recovering receivables. Cash entries are generated for cash sales or recovery of accounts receivable for credit sales.
Cash transactions are based on cash accounting. However, accrual accounting transactions also use cash receipts as and when received from customers.
Format of a Cash Receipt
A cash receipt can have a different format for each organization. However, it must include some key information points relevant to the cash transaction.
Some key points included in the cash receipt are:
- Name of the issuer (individual or company)
- The transaction date for cash entry
- A document identification number or serial number
- The name of the customer (individual or company)
- Amount received in cash (not necessarily transaction amount)
- Payment method; cash, bank card, or bank transfer.
- Signature of the receiver
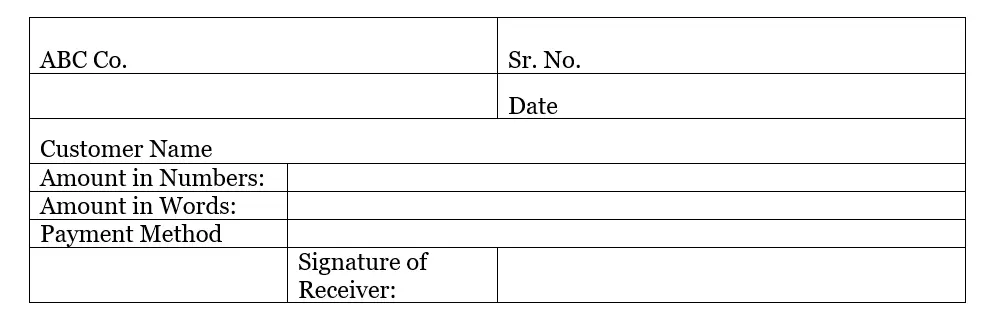
Important: The cash receipt format can vary by the nature or size of the business. A business can use relevant information points to be printed on the cash receipt.
Categories of Cash Receipt
A cash receipt can be issued for several transactions. Most commonly it is issued for cash transactions paid spontaneously by customers.
Cash Received from Cash Transactions
It is issued for all cash transactions received from customers. It is used to record the cash sales of products or goods. The receipt records the cash amount and customer name to create the journal entry.
Cash Received from Cash Receivables
A cash receipt can also be issued for cash received from credit customers. The transaction can include cash accounting as advance or recovery of credit sales.
Cash Received from Miscellaneous Transactions
Other cash transactions can include payment through a card or immediate bank transfer. A bank transfer can take a few days to complete.
Journal Cash Receipt Entry with Examples
Suppose a cashier for a grocery store collects cash payments for daily sales. The store includes a sales tax on the prices of products as well.
Assume a customer makes a purchase of $300. The sales transaction then adds a sales tax of 3% ($90). The total cash received is $390.
The journal entry for the cash transaction will be:
| Item | Debit | Credit |
| Cash | $ 390 | |
| Sales | $ 300 | |
| Sales Tax Payable | $ 90 |
The cash receipt issued for the cash transaction will look like this.

The store can issue similar cash receipts to its business customers when receiving cash.
Cash Receipt Journal
A cash receipt journal is an accounting journal that keeps a record of all cash transactions made by a business. It follows the rules of cash accounting and records a transaction as and when it completes.
Any credit sales are not recorded on a cash journal. It means it isn’t used by a business following accrual accounting methods.
A cash receipt journal records all types of cash transactions of a business. These transactions can include business sales, accounts receivable, interest, and other forms of cash payments.
Some common cash accounts used by a business that are recorded on a cash receipt journal include the following.
- Business retail or wholesale transactions to customers.
- Cash collections from credit customers (settlement of credit sales).
- Capital issued by owners
- Loan amounts received from the bank/creditors
- Investment income, rental income, or dividends received
- Other income received in cash such as commission, fees, tax refunds, etc.
Format of the Cash Receipt Journal
The general format of a cash receipt journal can look like the following.
| Date | Reference No. | Account Credited | Details | Cash DR | Sales Discount DR | Accounts Receivable CR | Sales CR |
| Total |
- Date: The first column is for the date entry. It is the date of receiving cash for any transaction.
- Reference No. It is the reference number for journal accounts used by the business. Each journal account should be given a unique reference number.
- Account Credited: In this column, the cashier will enter the credited account details.
- Details: This section will be used to enter particulars or explanations about the transaction. For instance, if the cash receipt is for a credit sales transaction made earlier at a later date now.
- Cash: It denotes the total cash amount received for the transaction. The account is debited to show the cash received entry.
- Sales Discount: It should record any sales discounts offered by the business.
- Accounts Receivable: This account is created to reflect the changes in credit sales. It records the customer reference as well as the amount received against receivables.
- Sales: This journal section records the cash sales amounts. Only cash sales made to customers are entered in this section.
Examples
Suppose ABC co. is a retailer of apparel and clothes. ABC has the following data regarding its cash sales for the month of August 2021.
- 07/08/2021 – Cash Sales made of $3,000.
- 12/08/2021 – Cash received from credit customer $450 after-sales discount of $20.
- 14/08/2021 – Cash Sales made of $2,000.
- 17/08/2021 – Cash received from credit customer of $1,000.
- 20/08/2021 – Loan from Bank $5,000.
- 22/08/2021 – Interest received on Bank account of $200.
- 25/08/2021 – Cash received from credit customer $ 300
The Journal entries for the cash receipt journal will be made in the following manner.
| Date | Reference No. | Account Credited | Details | Cash DR | Sales Discount DR | Accounts Receivable CR | Sales CR |
| 07-08-21 | 0821001 | Cash | Cash Sales | $ 3,000 | $ 3,000 | ||
| 12-08-21 | 0821002 | Credit Account | Credit Recovery | $ 430 | $ 20 | $ 450 | |
| 14-08-21 | 0821003 | Cash Sales | $ 2000 | $ 2000 | |||
| 17-08-21 | 0821004 | Credit Account | Credit Recovery | $ 1,000 | $ 1,000 | ||
| 20-08-21 | 0821005 | Bank Loan | Loan from bank | $ 5,000 | CR $ 5,000 Others | ||
| 22-08-21 | 0821006 | Interest | Interest Earned | $ 200 | CR $ 200 Others | ||
| 25-08-21 | 0821007 | Credit Account | Credit recovery | $ 300 | $ 300 | ||
| Total | $11,930 | $ 20 | $ 1,750 | $ 10,200 |
Uses of Cash Receipt
A cash receipt and a cash receipt journal are important for any business for maintaining its cash accounts. A cash receipt journal helps a business in maintaining cash flow records, journal entries, accounts receivable, bank account reconciliation, and preparation of financial statements.
A cash receipt is an important tool for businesses in legal compliance as well. Businesses can maintain sales tax or VAT records with the help of a cash journal.
