A capital partnership is a form of a tie-up where the member partners in the capital partnership share every part of the capital. In its simplest form, capital partnership occurs in a form of a joint account where all the forms of capital transactions are recorded.
Some other forms that are shared in a capital partnership account are profits sharing, interest payments, and initial capital contributions from all the partners. The partnership capital can exist between two or more partners.

The sharing of capital account between partners allows for the maintenance of trust, accountability, and transparency between all the Capital partners.
Explanation
A capital partnership occurs between two or more people when they agree to form a single business entity. The agreements of the capital partnership are agreed in advance either orally or are written in the contract. The profit-sharing agreement is also agreed upon beforehand between the partners.
How the profits are shared either depends upon how much capital each partner is contributing or a certain percentage that must be agreed upon by all the partners in a capital partnership.
The capital partnership was very common before the 1960s for investment firms, where the entire par pooled their capital together to invest.
Example
Consider a company 123 formed by three business partners named 1, 2, and 3. The total capital is thirty thousand dollars. Each partner contributed an equal amount of capital. So, each one of the three contributed ten thousand dollars. According to the agreement between partners, the profit share would be equal among all the partners. As a result, each partner would receive about a third of the profits from the venture. Furthermore, the account for the business is one and each partner has access to it. This is done to maintain transparency in the partnership.
Important rules of a capital partnership
The most important rules of a capital partnership are given in figure 1 below:
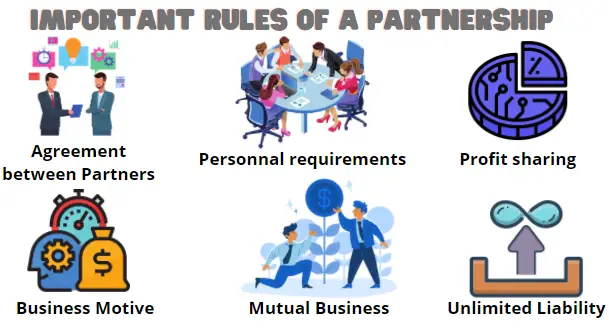
Figure 1: Six important rules of a capital partnership
The six important rules for a capital partnership are depicted in figure 1. The six rules to keep in mind are Agreement between partners, personnel requirements, profit-sharing agreement, business motive, mutual business, and unlimited liability. All six of these rules are further explained in detail below:
Agreement between partners
For a capital partnership to be formed there must be a mutual agreement between all the partners in the tie-ups. As explained before, the agreement can be oral or the agreement can also be a contract between all the partners. What method they choose depends upon the partners. It is always a good idea, though, to have a contract, just in case any disagreements surface in the future. At that time, an oral agreement cannot be of much help to any partner.
Personnel Requirements
The minimum number of personnel required to have a capital partnership is two persons. More than two people can also join a partnership, but the minimum requirement is for two persons to make a capital partnership. Usually, more than two people form a capital partnership.
To make the capital partnership a success, these two or more people must see eye to eye and have common goals, otherwise it is almost a given that the partnership would fail.
Profit sharing agreement
The profit-sharing agreement means how the profits obtained as a result of the capital partnership would be distributed. The profit-sharing agreements are agreed upon by all the partners, beforehand of forming a partnership or giving it a legal structure.
The usual method of profit-sharing agreement is that each partner receives profits that are equal to the percentage of capital contributed by that partner. But, in some rare cases, the profit share is different from the capital share.
This happens when one of the partners is just contributing capital and not any expertise. In this case, one partner brings the expertise, while the other partner brings the capital.
Business Motive
What is the motivation behind starting a capital partnership? What are the goals of the partners? Do they have clear goals in mind? Do they provide a clear path to profitability? These are all the questions that must be asked before two or more people enter a capital partnership.
By answering these questions, and having clear goals, the partners can increase the chance of success of their business. The motivations of all the partners must be clearly stated!
Mutual Business
When representing the capital partnership, the partners are also representing each other. This is what is meant by mutual business. All the capital partnership partners must keep this in mind. This not only improves the performance of a business but also increases the mutual respect the partners have for each other.
Unlimited Liability
This is by far the most important rule of a business partnership. A capital partnership unlike a corporate entity is unlimited liability in its legal structure. By limited liability, it is meant that the liabilities such as debt are not transferred to the shareholders of that business. The liabilities end at that business.
But in unlimited liability, the liabilities do not end at the business. In a capital partnership, the partners are liable for the liabilities which are on the business. If a business, which has a capital partnership agreement, goes bankrupt and the debt and other liabilities which the business owes are not completely paid off by selling the assets of the business, any other liabilities are transferred to the partners.
The unlimited liabilities aspect of the capital partnership means that any single partner would avoid taking any unnecessary extra risk. This increases the chance of success for a capital partnership.
Conclusion
The capital partnership is a sort of business partnership where each partner contributes a specific amount of capital into a business entity that has single account access to all partners which increases the transparency. The capital partnership reduces risk-taking which increases the chances of success of the capital partnership.
