Definition:
Budgeting is the process of estimation of revenue and expenses for the upcoming financial period in general that may be divided further into various divisions of quarters and months for periodic evaluation.
It could also be divided into many business divisions, departments, activities, lines of revenues as well as expenses.
Budgeting helps the user to forecast the revenue, expenses, profits, and more which could help them to know how they are going to earn and plan appropriately where they are going to spend the money earned.
Budgeting sets out the difference between the plan and reality. Budgets are made by every size of businesses be it small or big listed companies.
Importance of budget:
Good businesses allocate their time to create and manage budgets, prepare and review their plants. They regularly like to monitor the financial health of their enterprise. Budgeting helps to identify the current availability of capital, proper estimation of revenue, and anticipates cost.
Businesses with help of budgeting can concentrate on cash flows, reduction of costs, and improve financial metrics. The budget ensures that the business is able to meet its objectives and involve in taking confident financial decisions.
Budgeting helps to ensure that money is allocated to those things that support the strategic objectives of the business.
It sets out the priorities straight and helps in the constant achievement of the company’s milestones heading towards the vision of the company. It also helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of the company.
Contents of good budget:
Budgeting shall be flexible so as to withstand changing business circumstances. Good budgeting shall be able to depict the time required, goals, and cost of any business activity. The components of the budget are as follows:
Fixed costs
Fixed costs are those costs that do not change every year. These costs include various costs like rent, insurance, utilities, bank fees, accounting, and legal fees, and costs related to fixed assets for maintenance and so on.
Variable costs
These costs change regularly with production level. These costs are related to the cost of goods sold and include costs like raw materials cost, production costs, packing costs, etc.
The costs associated with selling including sales commission, travel costs, etc. The budget clearly depicts these variable costs.
One-time costs
The various businesses scuffle with one-time costs in their statement once in a while. It may be related to moving offices, replacing old furniture, equipment or computers. Further, one-time costs may also be related to researches or the launching of new products.
The cash flows
The movement of cash decides if your business is generating positive cash flows or there is an outgo of cash flows. The businesses must monitor the flow of cash to maintain the liquidity of the business to meet any emergency expenditure if needed.
Profits of business
Profit is the difference between revenue and expenditure. The increase in profits means that business is growing as well. Profit margins can be easily achieved when budgeting is done well.
The budget for small business typically look like this
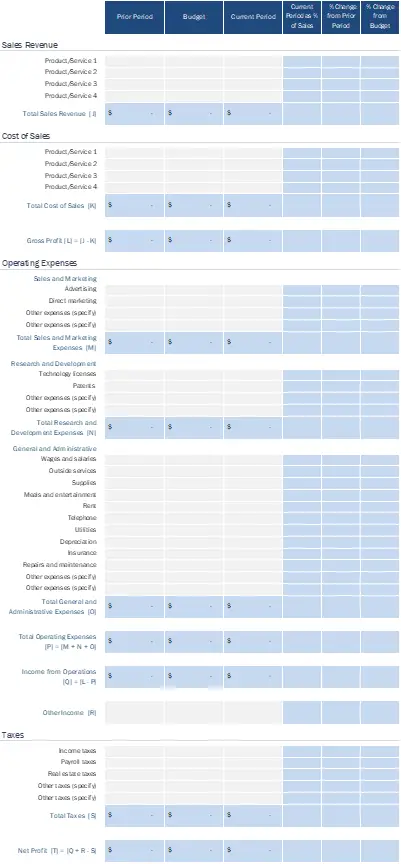
5 Processes of Budget
The budgeting process is simple. All the historical data is analyzed to form a budget for the current period. The expenses that will be new and any revenue alternations shall be provided for. The budget process has been explained below :
1) Make budgeting assumptions
The sales and cost trends shall be assumed based on empirical evidence of the past. These should be further reviewed on an ongoing basis just like the case that coronavirus pandemic would make some companies generate comparatively lower revenue.
2) Create clear process and workflow
The management shall create a visual workflow that should be clear as to the numbers to be achieved, manual checks, and interventions on the way. This will help the preparer to consolidate financial numbers well.
3) Use driver-based planning
This means using the sub-plots of budgeting contents in a more enhanced level of importance. The budget data must be broken into various components and in a way, those responsible for dealing with them shall be made accountable.
4) Testing the simulations and going live
Budgets are simply what’s going to happen on the front of income and expenditures. All the best and worst-case scenarios of the budget shall be compared with each member of the budget team.
It shall be simulated and well thought in advance which types of obstruction in the business environment will be evident in the coming period and how can the company handle it through simulations and then in a live environment.
5) Support with reasonable explanations:
The financial data of the budget sheet shall be well detailed and should be explained with all the notes. The notes shall be explanatory as to why and how the financial data has arrived and how it is going to change during the period of the budget.
